ISO 9001 Certified
Oil Refining Technique
Welcome to our webpage dedicated to oil refining techniques. Here, we provide comprehensive information on different oil refining techniques. Our team of experts has extensive knowledge and experience in the industry, and we are committed to sharing our expertise with you.
What Is Oil Refining And Process
The process of removing the gums, pigments and bad smell in the edible oil is called as refining.
The crude oil mainly contains mainly mixed fatty acid triglycerides, commonly known as neutral oil is removed. Phospholipids, free fatty acids, pigments, peroxides, waxes and various mechanical impurities are removed. The presence of these impurities can have a detrimental effect on the storage, consumption or processing of fats and oils.
Refining main processes
Degumming
The process of removing colloidal impurities from oil is called degumming, and the colloidal impurities in crude oil are mainly phospholipids, so the oil mill often refers to degumming as dephosphorization. Degumming methods are hydration method, heating method, acid method and adsorption method.
Deacidification
The process of removing free fatty acid in the oil.it has alikaline refining method and distillation method. From the alkaline refining method, you can get soapstock. For the distillation method, normally together with deodorization process.
Decolorization
There are many methods of oil decolorization, the most widely used in industrial production is adsorption decolorization method.
Adsorption decolorization: the use of adsorbent adsorption grease pigment and other impurities, by filtering to remove the adsorbent and impurities, to achieve the purpose of grease decolorization and purification.
Adsorbent: ① natural bleaching clay, acidic, also known as acidic white clay; ② active white clay, bentonite clay as raw material processed into a more active adsorbent, has a strong adsorption capacity, in the grease industry decolorization is widely used; ③ activated carbon, the ratio of activated carbon and active white clay is 1: (10 ~ 20).
Adsorption temperature:80~110℃, generally controlled at 80℃~85℃.
Stirring speed: ≤80r/min, decolorization time: 10~30 min
Adsorbent dosage: the amount of white clay is 1% to 3% of the oil weight
Deodorization
The purpose of deodorization: mainly to remove the substances that cause odor in the oil. To remove these bad odor process called deodorization.
Deodorization is the most important step in the oil refining process.
Deodorization reasons:
- The presence of odor substances
- Partial pigment residue
- Remove the free fatty acid
Deodorization principle: Water vapor stripping under high vacuum and temperature condition.
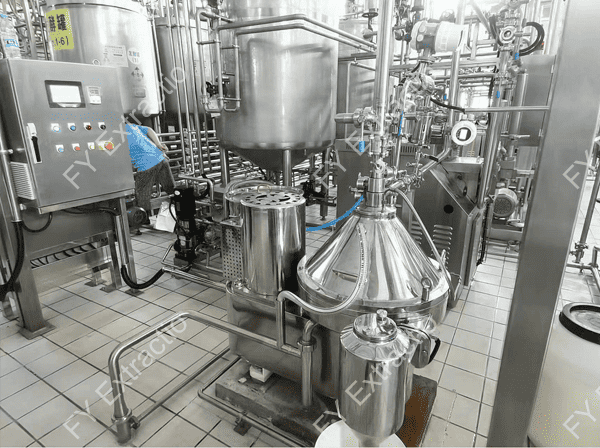
Explore FY Extractio's Solution
Oil Refining Glossary
oils and fats refining
Also known as “refining”. A collective term for a series of procedures to remove solid impurities, free fatty acids, phospholipids, gums, waxes, pigments, odors, etc. from vegetable oils.
mechanical refining
The method of removing solid impurities and some colloidal impurities from crude oil by precipitation, filtration, centrifugal separation, etc.
physical refining
Also called “distillation deacidification”. Refining method of removing free fatty acids by distillation under high temperature and high vacuum by the difference in relative volatility of triglycerides and free fatty acids.
chemical refining
A method of refining fats and oils by adding certain chemical substances, such as alkali refining, acid refining.
physical-chemical refining
Refining method to remove impurities in oil by physical-chemical reaction, such as hydration, adsorption decolorization, deodorization, etc.
miscella refining
Refining method of removing oil and grease concomitants such as cotton phenols, free fatty acids, waxes, etc., and then removing solvents from the oil.
crude oil
Unfiltered oil obtained by pressing or leaching.
filtered crude oil
Crude oil obtained by precipitation and filtration to remove solid impurities.
refined oil
A general term for the oil that meets the standard after one or more refining processes.
oils and fats
A generic term for triglyceride esters of fatty acids. Natural oils and fats are mixtures of triglycerides of mixed fatty acids, generally called oils and fats if they are liquid at room temperature.
protein
A polymer compound consisting of hundreds of thousands of amino acid molecules condensed together.
carbohydrate
Also called “carbohydrate”. A general term for a class of polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, as well as their condensates and certain derivatives. It is usually divided into monosaccharides, polysaccharides, etc.
phosphatide/phospholipid
Short for phosphoglyceride, commonly found in plant seeds and animal tissues, insoluble in acetone. The main forms are ceruloplasmin and lecithin, etc.
wax
Mainly refers to esters synthesized from higher monohydric alcohols and higher fatty acids.
sterol
Also called “steroid”. A cyclopentane containing hydroxyl groups and all-hydrophilic compounds.
gossypol
A dark and toxic polyphenol unique to cotton seeds, under certain conditions free cotton phenol will become denatured cotton phenol or bound cotton phenol.
vitamin E
A light yellow viscous oily liquid with antioxidant properties.
antioxidant
A substance that prevents or delays the oxidation and rancidity of oils and fats.
pigment
A substance that has its own color and can bring color to oil or grease.
unsaponifiable matter
A substance contained in a grease that cannot react with alkali. Such as high grade alcohols, waxes, etc.
solid impurities
The mud, sand, material fines powder, fiber, grass straw and other solid impurities mixed in the crude oil.
oil soluble impurities
A type of impurities soluble in oil. Such as free fatty acids, pigments, sterols, vitamin E, hydrocarbons, etc.
mucilaginous impurities
Proteins, sugars, resins, mucilage and other gelatinous substances present in oil.
free fatty acid
The fatty acid in the unripe oil seeds which has not been synthesized ester and the fatty acid which is free in the oil produced by moisture, heat, the action of lipolytic enzymes and the oxidation and decomposition of oil.
oil residue
Precipitation, filtration of crude oil and oil press residue.
oil sediment
The precipitate of the oil after hydration.
soapstock
The sediment of crude oil after alkali refining.
pre-purification of crude oil
The process of removing the solid impurities contained in crude oil.
precipitation
The process of separating solid particles suspended in grease by natural sinking.
filteration
The process of removing solid impurities from crude oil by passing it through a filtering medium under the action of gravity or power.
hydration
A process in which a certain amount of water or an electrolyte solution such as dilute salt or alkali is added to hot oil with stirring to cause colloidal impurities in the oil to coalesce and precipitate and separate.
settling
The oil is left at a certain temperature for a certain period of time to ensure that the phospholipids in the oil are fully precipitated.
drying
The process of removing the small amount of moisture still contained in the hydrated oil under atmospheric pressure.
raw phosphoilpid
The mixture that is separated or precipitated from the hydration equipment.
neutral oil recovery
The process of recovering the neutral oil contained in the oilfoot or soapstock.
emulsion
An emulsion in which the oil is difficult to separate from the phospholipids or soap particles due to improper handling in the hydration or alkali refining process.
salt breaking emulsion
A method of separating an emulsion or colloidal solution by adding metal salts to the solution.
acid degumming
A refining method in which a certain amount of acid is added to the crude oil to remove colloidal impurities such as protein mucilage.
phosphoric acid degumming
A method of degumming by adding phosphoric acid to crude oil.
de-acidification
The process of removing the free fatty acids contained in the crude oil, and the methods of deacidification include alkali refining, water steam distillation, solvent extraction, etc.
caustic refining/alkali refining/neutralization
A refining method that uses alkali such as caustic soda and soda ash to neutralize the free fatty acids in the oil to produce soap feet that are precipitated and separated from the oil.
continuous caustic refining/continuous neutralization
Continuous caustic refining method in which oil and alkali mixing, neutralization, desaponification, washing and dehydration processes are carried out continuously.
batch caustic refining/batch neutralization
Discontinuous alkali refining method.
refining yield
Refined oil as a percentage by weight of the filtered crude oil consumed.
refining with high temperature and thin alkali
An alkali refining process that utilizes a high preheat temperature and a low amount of superalkali during neutralization. It is suitable for low acidity, light colored crude oil produced by high moisture evaporation.
refining with low temperature and thick alkali
A kind of alkali refining process with low preheating temperature and high super alkali amount during neutralization. It is suitable for gross oil with high acid value and dark color.
degumming-alkali refining technics
Degumming and dephosphorization are carried out first, followed by alkali neutralization. It is used when the colloidal impurities in the crude oil often cause emulsification, resulting in increased refining consumption, and when pre-degumming and dephosphorization are sometimes required.
washing
A method of washing the trace soap particles suspended in grease with water during the alkali refining process.
vacuum drying
A method of removing water from grease under negative pressure.
neutralization tank
Also called “alkali refining tank”. A type of refining tank used for intermittent alkali refining.
soapstock tank
Equipment used to process soapstock to recover neutral oil.
bleaching
Refining process to remove some pigments and residual substances that are not removed in the alkali refining process to improve the color and quality of oil and grease.
adsorption bleaching
A method of removing pigments from oil and grease by using adsorbent agent.
adsorbent/adsorbing agent
A substance with strong selective adsorption, commonly used are natural bleaching earth, activated white earth, activated carbon, etc.
activated bentonite
The bentonite is used as raw material, and it is made by coarse crushing, acid activation, washing, drying, grinding, sieving, etc. It is a highly active adsorbent used for oil and grease decolorization.
filter aid
A substance that can improve the filtration efficiency of filtrate.
deodorization
A refining process that removes odoriferous substances from fats and oils.
steaming deodorization
When water vapor is passed through the oil containing odor components, the vapor-liquid surface comes into contact and the water vapor is saturated by the volatile odor components and escapes in proportion to its partial pressure to remove the odor from the oil.
batch deodorization
The whole deodorization process is discontinuous and is generally divided into several steps: deodorization, cooling, and filtration.
continuous deodorization
The whole deodorization process is continuous deodorization of oil and vapor steam in counter-current contact.
conduction oil
Highly stable, non-toxic, odorless heat transfer medium oil.